In this world where developers and SRE strive to ship their applications to various environments in an agile and efficient way. Docker an open-source tool has emerged as a game-changer. Docker is a fantastic tool to scale up an application's productivity, delivery, and maintainability.
In this article, we will understand docker and Dockerize a Python flask application.
if you are an absolute beginner and want to get hands-on with Docker then this Article is for you!!
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that automates the deployment of applications inside lightweight, portable containers. These containers encapsulate all the necessary components required to run an application, including the code, runtime, libraries, and system tools. Docker containers can be executed consistently on any system that supports Docker, regardless of the underlying infrastructure.
At its core, Docker relies on containerization technology, a method of packaging and isolating applications and their dependencies, making them easy to manage and deploy. Docker containers share the host operating system's kernel, which means they are highly efficient and consume fewer resources compared to traditional virtual machines.
Key Components of Docker
Docker Engine: This is the heart of Docker, responsible for building, running, and managing containers. It includes a server, REST API, and a command-line interface (CLI) that enables users to interact with Docker.
Docker Image: Images are read-only templates that contain everything needed to create a runnable instance of an application. Developers create images to package their applications and dependencies.
Docker Container: A running instance of a Docker image is called a container. Containers are isolated from each other and the host system, ensuring that they don't interfere with one another.
Docker Compose: Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container applications. It allows you to specify the services, networks, and volumes required for your application in a single file, making it easy to manage complex deployments.
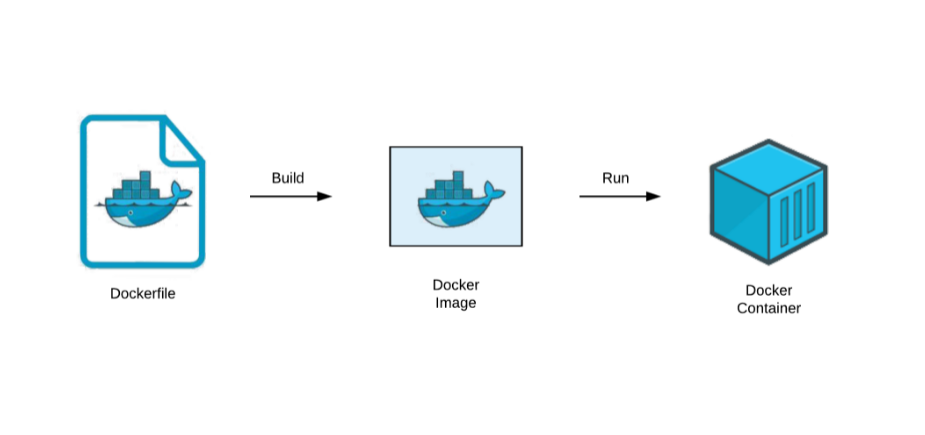
Now that we know about docker, let's get our hands dirty
Dockerizing Python Flask Application

Installing Docker
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/
This should be pretty much self-explanatory on how to install
Check docker Version
Docker -v
Doceker init
This will return the current version of docker installed

Creating Flask-app
To get started create a folder for your Application
mkdir Sample_flask
cd Sample_flask
Now let's understand the files we are going to need

main.py - Here is where our flask application will be written
template/index.html - HTML for flask application
Dockerfile - This will provide instructions on how a docker image should work
requirements.txt - includes all the Python module dependencies
Before we get started creating a flask application let's install it
pip install Flask
from flask import *
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template("index.html")
if __name__=="__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
Index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="">
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="text-align: center;";>Welcome to Docker</h1>
<p style="text-align: center;"> Lets learn Dockerize a Flask Application</p>
<script src="" async defer></script>
</body>
</html>
Requirements.txt
To create a Requirements.txt automatically
pip freeze | findstr Flask >> requirements.txt
Flask==2.3.3
Now before we create a docker file let's run this Flask application
python main.py

And it works!

Now we are all set to create the App , Let's create Dockerfile
Dockerfile
FROM python:3.8-slim-buster
WORKDIR /sample_flask
COPY requirement.txt requirement.txt
RUN pip install -r requirement.txt
COPY . .
CMD ["python","main.py","host=0.0.0.0"]
Before we proceed to create an image let's first understand what lines we wrote in our Dockerfile and what role they play.
Docker allows us to other existing images. we can create a base image to import from but in this case, we are using a Python image
FROM python:3.8-slim-buster
WORKDIR specifies which directory to use, here we are telling docker to use Sample_flask as the working directory
WORKDIR /sample_flask
COPY and RUN, We are telling Docker to create a copy of requirements.txt in the docker image and run the install command
COPY requirement.txt requirement.txt
RUN pip install -r requirement.txt
COPY . . it copies the remaining files to the docker image
COPY . .
CMD tells what command this image inside a container
CMD ["python","main.py","host=0.0.0.0"]
Build a Docker Image
We are all set to build a docker image now.
we will use docker build to create an image, combined with -t/-tag we can specify the image name
docker build -t flask-docker .
Now let's check if your image is built or not using docker images, this will return the list of images built
docker images

we have successfully created a docker image
Now let's run this image as a container using the docker run command
docker run [image_name]
docekr run flask-docker

and that's it! you have your container running
To check the currently running container
docker ps

Stop the container using
docker stop [contianer-name]
Congratulations!! we have created a docker image and ran a container
Thank you all for following through, this is my first Technical article and I hope to write more
You can connect with me on Linkedin

